DFT MLFF CFF Speed Accuracy Transfer
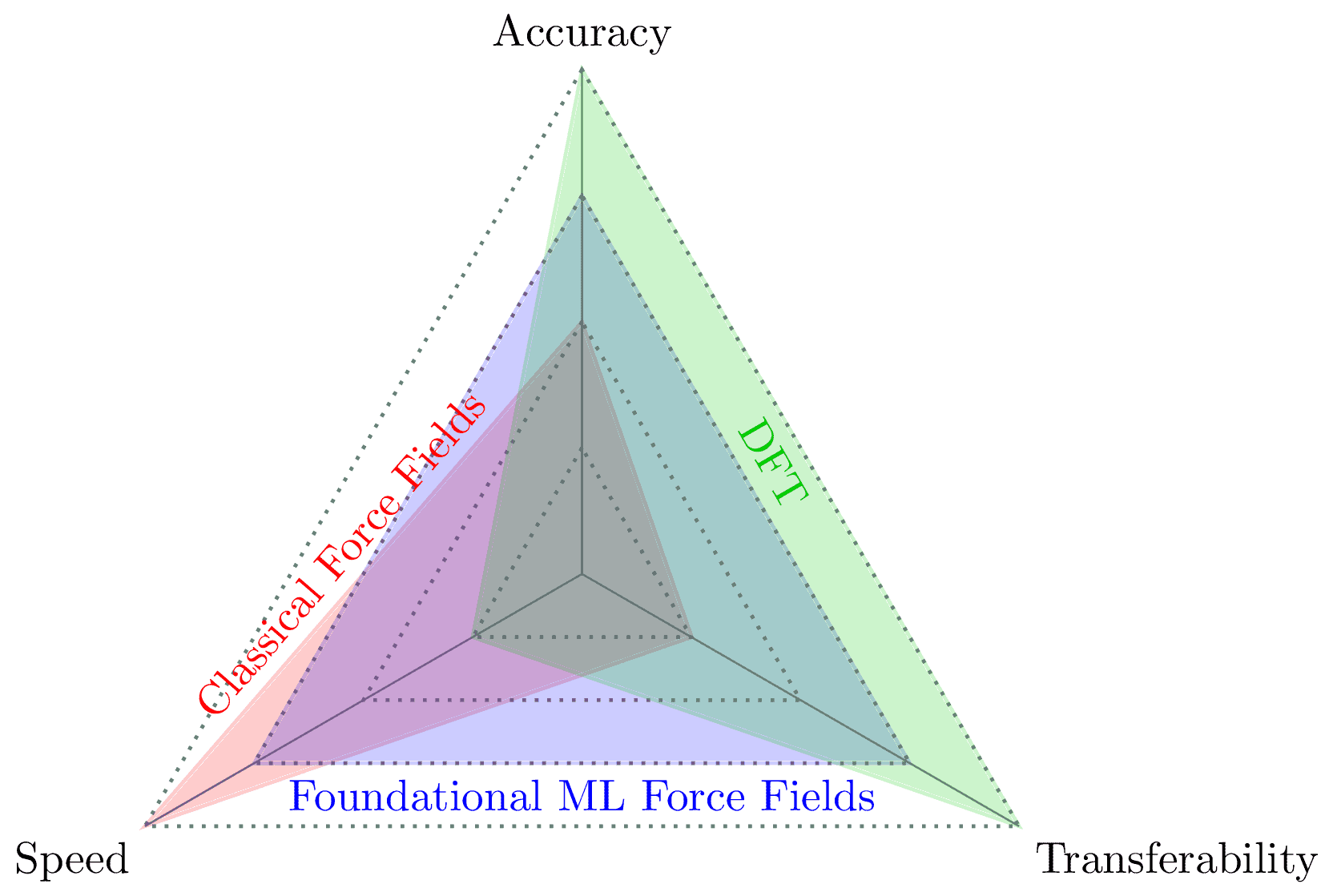
This spider diagram compares three computational chemistry methods: Classical Force Fields, Foundational ML Force Fields, and Density Functional Theory (DFT). The comparison is based on three key attributes:
- Accuracy: The precision and reliability of the method's predictions.
- Speed: The computational efficiency and time required for simulations.
- Transferability: The ability to be applied across diverse chemical systems and material classes.
- Classical Force Fields (red): Highest speed, medium accuracy, lowest transferability.
- DFT (green): Highest accuracy and transferability, but lowest speed.
- Foundational ML Force Fields (blue): Balanced performance across all attributes, positioned between classical methods and DFT.
This diagram shows common trade-offs, highlighting how Foundational ML Force Fields aim to bridge the gap between the speed of classical methods and the accuracy of DFT, while offering improved transferability over classical force fields.
Download
Code
dft-mlff-cff-speed-accuracy-transfer.typ (56 lines)
dft-mlff-cff-speed-accuracy-transfer.tex (32 lines)